Choosing between laser welding and MIG welding technologies is tricky due to their advantages even though they both use different machines, have different accuracy, and produce welds of different quality.

To choose from the two, you should consider several factors and this article is your guide on the laser welding vs MIG welding comparison as it explains both processes so you can choose better.
What is Laser Welding?
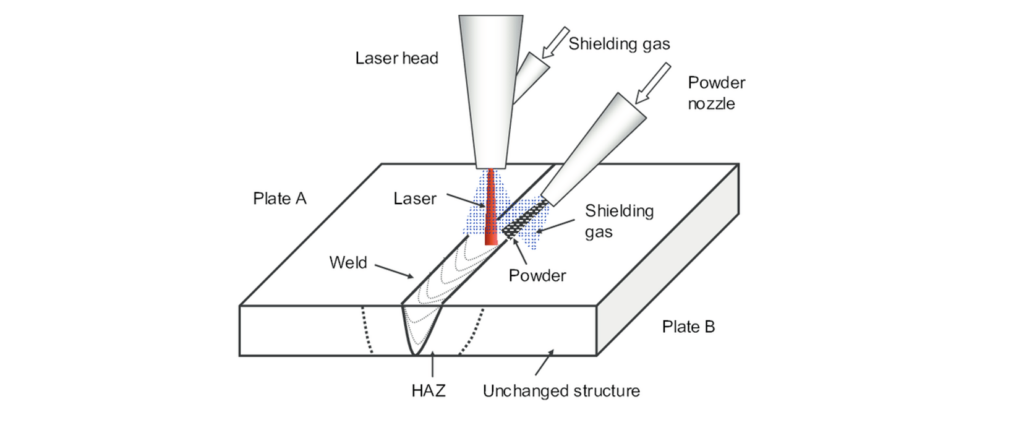
Laser welding is a welding technology that uses a concentrated laser beam to join workpieces together. The laser beam generates heat that melts the joint of both parts and on solidification of the molten surface, a welded joint forms. Filler materials are also popular in the welding process to create a stronger welding joint especially when joining dissimilar materials.
Process in Laser Welding

Common processes in laser welding are:
- Keyhole Welding
In keyhole welding, a high-power laser is used to heat a part to a high temperature creating a deep hole (keyhole) suitable for joining thin parts.
- Laser Brazing
In laser brazing, you heat the workpiece together with a filler to form a molten surface which on cooling forms a strong welded joint. It is applicable in welding two parts made of dissimilar materials.
- Heat conduction welding
Here, you use a low-power laser to generate a laser beam that heats the parts’ surfaces beyond their melting point. It produces moderate weld strength but aesthetically appealing welded joints making it unsuitable for parts that require strong welded joints.
Advantages of Laser Welding

Laser welding has the following advantages over other welding technologies:
- Accuracy
Laser welding is accurate because the focused laser beam touches only the desired area to create small welds. In a non-CNC system, the machinist has full autonomy over the welding operation making the process suitable for welding delicate parts.
- Speed and Flexibility
Laser welding operations are fast and flexible. You can adjust the laser parameters to suit different operations including welding inaccessible areas, and thin and thick pieces.
- Material Compatibility
Laser welding is compatible with joining parts metals, plastics, ceramics, and composite materials. Additionally, you can use it for joining dissimilar materials such as nickel-titanium, stainless steel-copper, and copper-aluminum.
- Great Welding Depth
Keyhole laser welding can penetrate the joints, melting them and allowing the two parts to come together better and create a deep and narrow weld.
Cons of Laser Welding

Laser welding also has the following limitations:
- Cost
Laser welding technology requires huge capital investment for businesses that want to set up a complete welding system. As a result, many consider outsourcing their laser welding needs.
- Brittleness
Rapid cooling of the molten joint can lead to brittleness after cooling. These welded joints can crack and break under high-stress conditions.
- Safety
Laser welding machines emit harmful fumes and radiation which are unsafe to the operator. You can avoid these by adhering to safety measures such as wearing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) during welding.
Application of Laser Welding
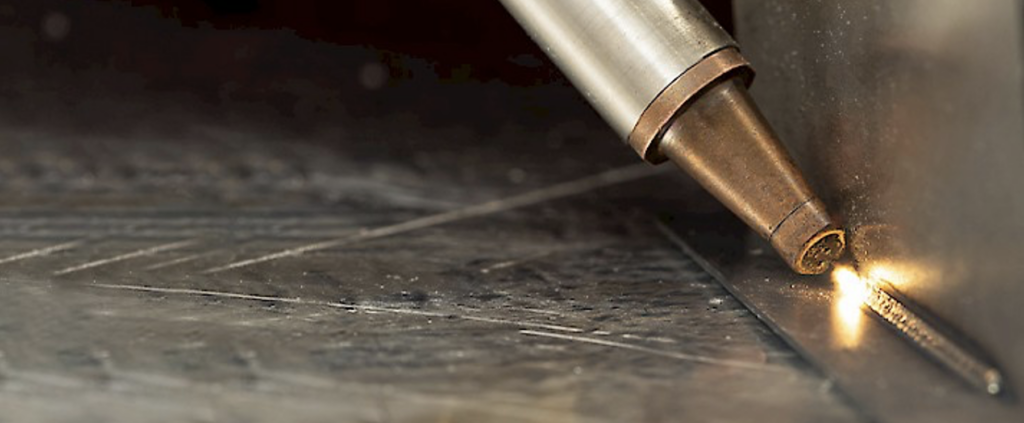

Laser welding precision makes it applicable in the following industries:
- Automotive Industry
Laser welding is used for joining the monocoque car chassis and sealing fuel tanks.
- Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry uses laser welding to join aluminum parts used in making structural engine components.
- Medical Part Industry
Useful in the manufacture of medical devices such as implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment.
- Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry uses laser welding due to its precision and power control for joining electronic components like connectors, batteries, and sensors
- Jewelry Making
Laser welding’s precision, non-contact process makes it the preferable welding technology for joining or fabricating jewelry made of materials like gold, silver, and platinum.
What is Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding?
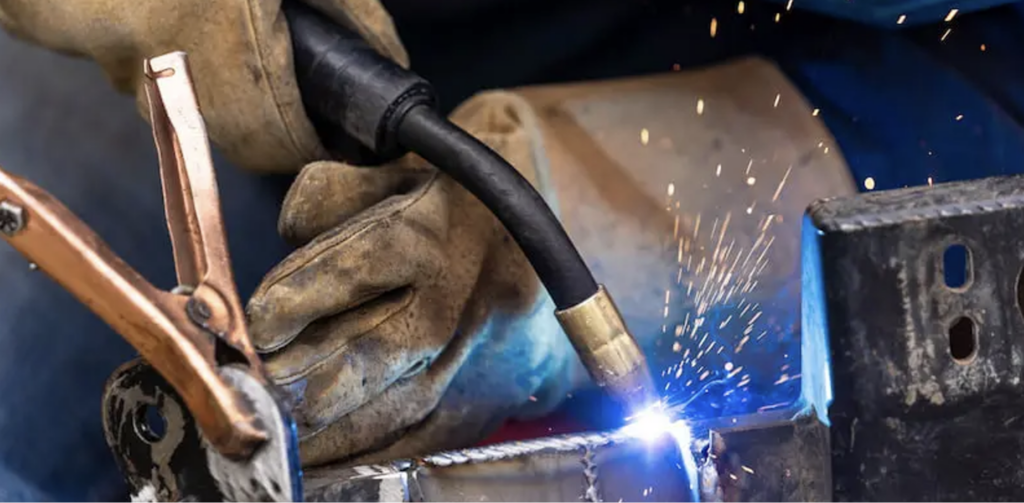

MIG welding involves using a consumable wire electrode (filler) which serves as an electrode and is fed continuously through the welding gun. When the electrode comes in contact with the base metal it produces an electric arc that melts the parts and the wire electrode, creating a weld pool which on cooling forms the welded joint.
MIG welding makes use of argon and carbon dioxide as shielding gas that protects the molten weld pool from oxidation responsible for cracks and weak welds. Furthermore, it makes use of direct current which creates a stabler electric arc and gives a finer welding output.
Advantages of MIG Welding

MIG welding offers the following benefits over other welding techniques:
- Process Simplicity
The MIG welding process is simple and can be easily used by beginners. Also, the MIG machine can be automated and there are fewer settings to adjust. This means it requires a few minutes to prepare the operators and they can further learn on the job.
- Clean Welds
MIG welding produces very clean welds that can be attributed to the shielding gas and operator experience and control.
- High Productivity
MIG welding is production efficient because the wire electrode continuously runs through the gun and reduces stop-start activities.
- Material Compatibility and Versatility
MIG welding is compatible with aluminum, magnesium, copper, and steel and its semi-or fully automated nature allows it to accommodate different needs and preferences.
Cons of MIG Welding

MIG welding has the following limitations:
- Environmental Influences
The environment may be a deciding factor in when to carry out MIG welding operations. For example, welding in windy conditions can reduce the shielding gas efficiency resulting in welds of weak or low quality.
- Limited Positions
MIG welding is better suited for horizontal operations because the heat input leads to a high liquid metal flow rate. For vertical processes, there may be overruns before solidification begins.
- Set-up and Maintenance Costs
The MIG welding technology also requires huge capital investment for businesses that want to set up a complete welding system. As a result, many consider outsourcing their laser welding needs.
Applications of MIG Welding
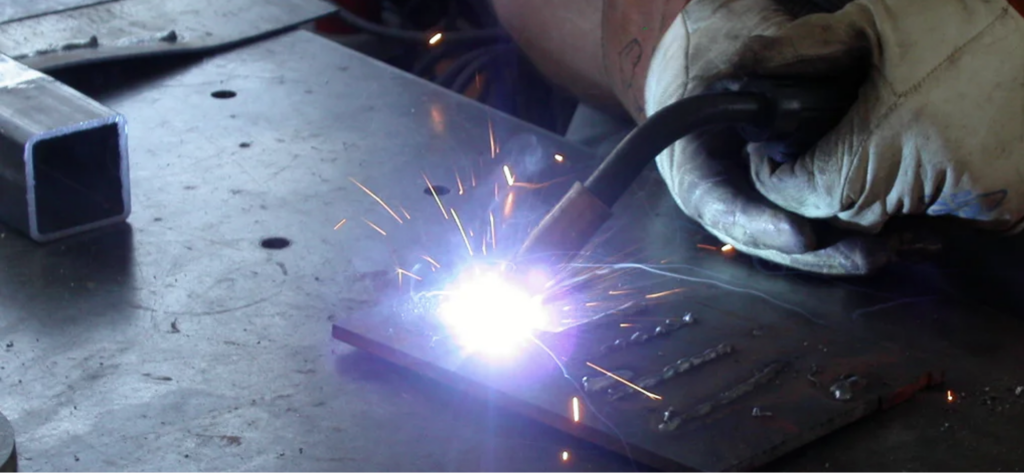

MIG welding is used in the following industries:
- Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, MIG welding is applicable in making car frames, exhaust systems, and welding body panels.
- Shipbuilding and Marine Industry
The shipbuilding and marine industry uses it for welding structures like decks, bulkheads, and pipelines.
- Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, MIG welding is used for welding structural parts like engine components and fuel tanks.
- DIY and Hobbyist Projects
DIY enthusiasts and hobbyists use MIG welding for personal projects like metal building, artwork and sculptures, and home improvement tasks.
- Pipe Welding
In oil and gas, plumbing, etc., MIG welding is used for welding pipes of materials like stainless steel and carbon steel.
Differences Between Laser Welding and MIG Welding

MIG and Laser welding differ in many aspects. The major differences between both processes are:
Materials
MIG welding is generally for medium-thick metals (0.6mm to 14mm) and is not compatible with other materials such as plastics, ceramics, and composites, unlike laser welding technology.
Equipment
A basic difference in the laser welding vs MIG welding comparison is their machines. MIG welding machines have a component like the welding gun, power source, wire feeder, cooling unit, grounding cable, and shielding gas tank while a typical laser welding machine has a laser source, beam delivery system, cooling system, and workpiece manipulation system.
Ease of Operation
Laser welding is easier to use because its machine comes in different sizes and designs to suit individual laser welding needs. For example, there are portable laser welding machines that are suitable for large parts with complex designs. On the other hand, MIG welding machines are typically larger which makes it difficult to move or work on hard-to-reach areas.
Heat Source
Another laser welding vs MIG welding comparison is the heat source. In laser welding, the laser beam generates the heat that melts the workpiece while in MIG welding, the electric arc formed by the wire electrode when it touches the workpieces generates the heat.
Heat Input
A major difference between MIG and laser welding is the heat input, i.e., the amount of heat supplied to the workpiece. MIG welding has a higher heat input than laser welding. As a result, there is a higher risk of defects and high heat-affected zones.
Weld Quality
Laser welding produces welds of higher quality characterized by no cracks, holes, or discoloration. On the other hand, MIG welding produces bigger welds which are prone to defects.
Precision
Laser welding has a higher level of precision and accuracy because the laser operator has more control and focuses the beam on a tiny spot to create more accurate and precise welds.
Workpiece Thickness
Laser welding is preferable for thin materials and requires high laser power as the material gets thicker. While you can increase the laser power as the thickness increases, MIG welding is the better option because it is more powerful and generates a deeper weld pool.
Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
Laser welding produces a smaller heat-affected zone because of the small spot size and control of the laser beam. On the other hand, MIG welding is characterized by a large heat-affected zone due to the high heat it produces, larger welding area, and lesser control.
Fumes Generation
Laser welding generates fumes, dust, and radiation during the process which makes it a less safe option than MIG welding which produces lesser harmful fumes and radiation. Nevertheless, MIG welding is prone to electrical, noise, and fire hazards.
Risk of Burn-through
There is a higher incidence of burn-through with MIG welding because it generates high heat which can penetrate the workpiece surface. Burn-through is not common in laser welding and only occurs when working with an unknown machine or unoptimized welding parameters.
Automation
Many laser welding machines are more automated than MIG machines. This means they require little human intervention with the laser head moving mechanically as the computer directs it to create precise welds. Most MIG welding operations are semi-automated because a fully automated MIG welding robot is very expensive.
Consumables
MIG welding uses more consumables when compared to laser welding as there is a need to regularly replace nozzles, gas diffusers, shielding gas, wire electrodes, contact tips, liners, etc. Consumables used in laser welding are lesser and examples are lenses and cutting heads.
Production Efficiency
The production efficiency depends on the application. Laser welding can be more production-efficient than MIG welding in joining small and thin. However, when joining thick parts, MIG welding can be more production efficient.
How to Choose the Right Process for Your Application

By understanding the difference between laser welding and MIG welding, you have an idea of choosing the most appropriate method. However, this might not be easy. Hence, you should answer the questions below to narrow your choice down:
What is the material thickness?
When working with thick materials and looking for a quality weld, the best choice is the MIG welding process. Unlike laser welding only suitable for thin materials and delivers lower weld quality with thicker ones, MIG welding produces a high heat suitable for these types of materials. The thickness of the material you are working with.
What is the operator’s skill set?
You should also consider the skill sets of the operators, especially for businesses that have the two welding technologies. Laser welding requires lesser human involvement due to automation and is better for not-so-experienced operators. This is unlike MIG welding where the operator experience will largely affect the weld quality.
What is my budget?
Your budget will determine the choice of welding technology you get as laser welding is costlier than MIG welding. However, you can enjoy a cost-effective welding process with either when you outsource to a welding service provider.
What surface quality do I desire?
Laser welded parts have a higher surface quality due to the lower heat-affected zones, unlike MIG welding. Hence, you should choose laser welding if this is very critical to the part functions or aesthetics
There is no straightforward approach to choosing the best welding technology. As a result, the points above can only act as a guide. Generally, MIG welding is better for thicker metals and creates strong welds at a relatively cheaper price while laser welding works best with thin and delicate metals, producing small and aesthetically pleasing weld beads with minimal heat input.
Zintilon Support for Your Welding Service
After deciding on the welding technique, you are going for, the next step is to choose a reliable third-party manufacturer. At Zintilon, we offer every type of welding service to meet our clients’ demands.
Our expert team members can examine your project requirements and offer recommendations on the best welding process. Our advanced welding machines and facilities are also compatible with parts of varying shapes, sizes, and materials.
We have more than 20 years of experience rendering welding services to clients in more than 50 countries and with us, you can get the best prices at a short lead time. Contact us today.
Conclusion
Laser welding and MIG welding processes can both create strong and high-quality welds but differ in many ways. This article did a laser welding vs MIG welding comparison, as it talks about their process, pros and cons of both processes, applications, differences, and how to use the right method for your project. Feel free to contact us for further questions and clarifications.
FAQs
Can Laser Welding and MIG Welding Be Used Together?
Yes, one can use laser welding and MIG welding together and enjoy the benefits of both processes. Also known as laser hybrid welding, it is used in the automotive, shipbuilding, and medical industry.
Is laser welding as strong as MIG welding?
MIG welding is stronger than laser welding and in a single pass can weld thick joints.
Can traditional welding methods join dissimilar materials?
Traditional welding methods including MIG welding, fusion arc welding, and shielded metal arc welding can join dissimilar materials. However, it is tricky if the difference in properties between the two materials is high. You can avoid this by using a filler material.




